

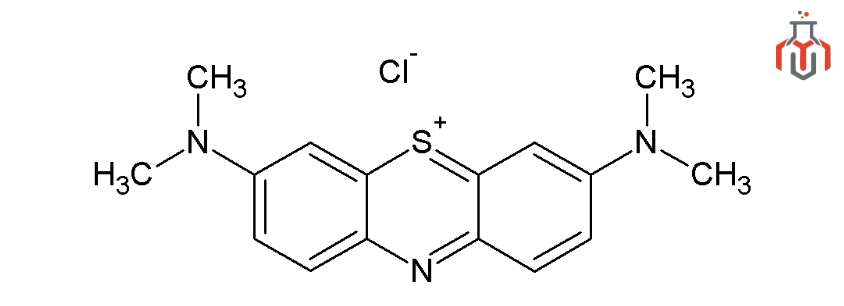
Methylene blue (MB), also called Methylthioninium chloride, is a tricyclic phenothiazine that belongs to the phenothiazine family. It’s a dark green powder that turns into a blue solution when dissolved in water. It is widely used as a redox indicator in chemistry because of its property of turning blue when oxidized and colorless when reduced. It is a primary treatment for methemoglobinemia, malaria, and many other pathogenic diseases. Notably, it was the first synthetic compound used as a clinical antiseptic.
CAS No.: 61-73-4; 122965-43-9
Synonyms: Methylthioninium Chloride, Basic Blue 9, Zinc free Methylene Blue, Methylene Blue Trihydrate
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C16H18N3SCl |
| IUPAC name | [7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium;chloride |
| Molecular weight | 319.85 g/mol |
| Solubility | Water, Glacial acetic acid, Glycerol, Ethanol 2%, & acetone 0.5% |
| Insoluble | Xylene & oleic acid |
| Flash point | 49°C [120°F] |
| Density | 1.230/cm3 |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Green |
| State | Crystal or powder |
| Melting point | 100-110°C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00000013(mmHg) |
| pKa | 7.5 |
| Vapour density | 1.59 at 20°C |
| pH | ~ 3 (in aqueous solution: 10 g /l, 20 °C) |
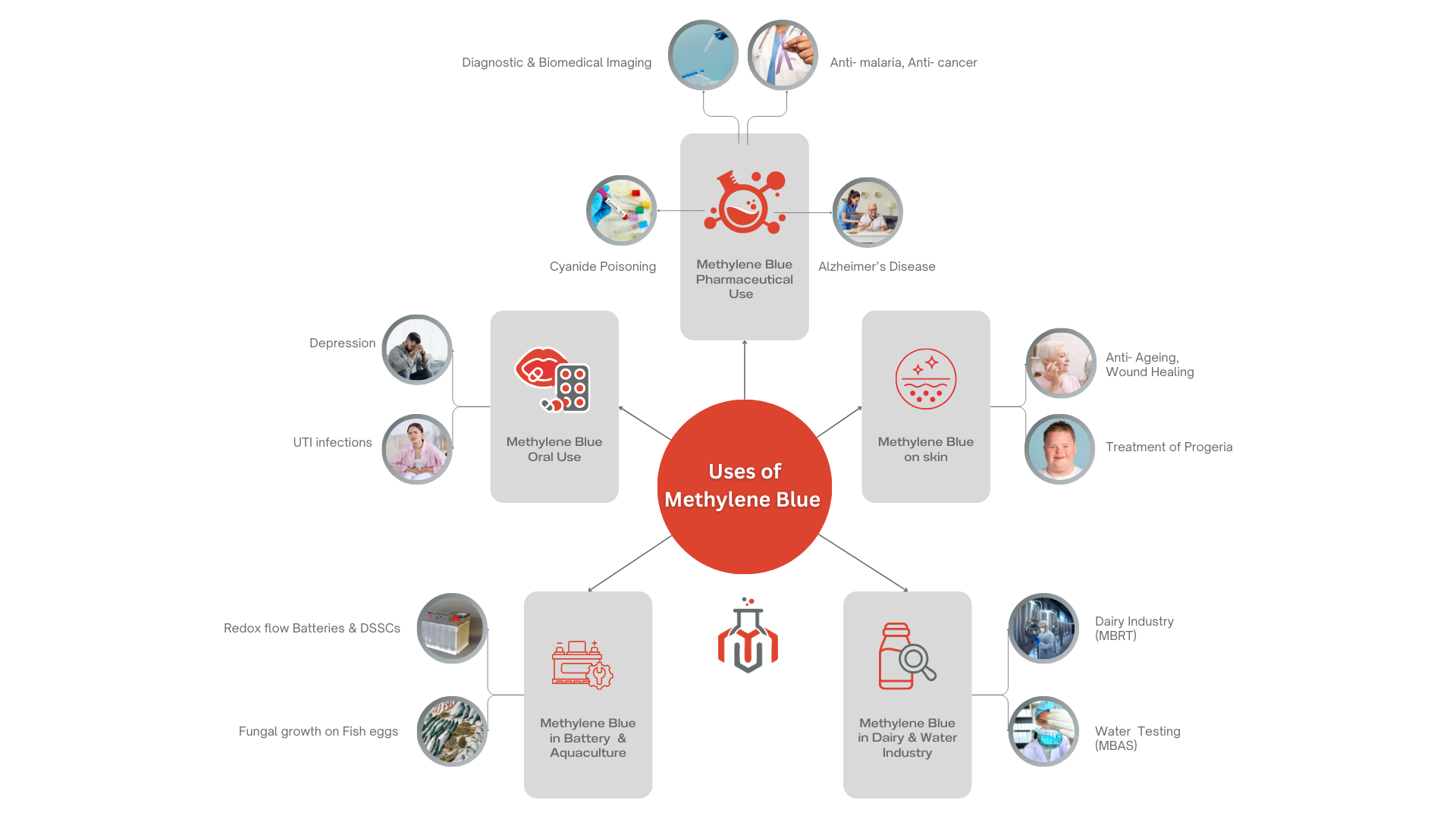
Methylene Blue slows down the aging effects of skin as it has antioxidant property. It stimulates fibroblast proliferation & promotes wound healing. It also increases the skin thickness and hydration. Studies are undergoing to check the potential of methylene blue in treatment progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome).
There are different side effects associated with the use of Methylene Blue depending upon the route of administration.
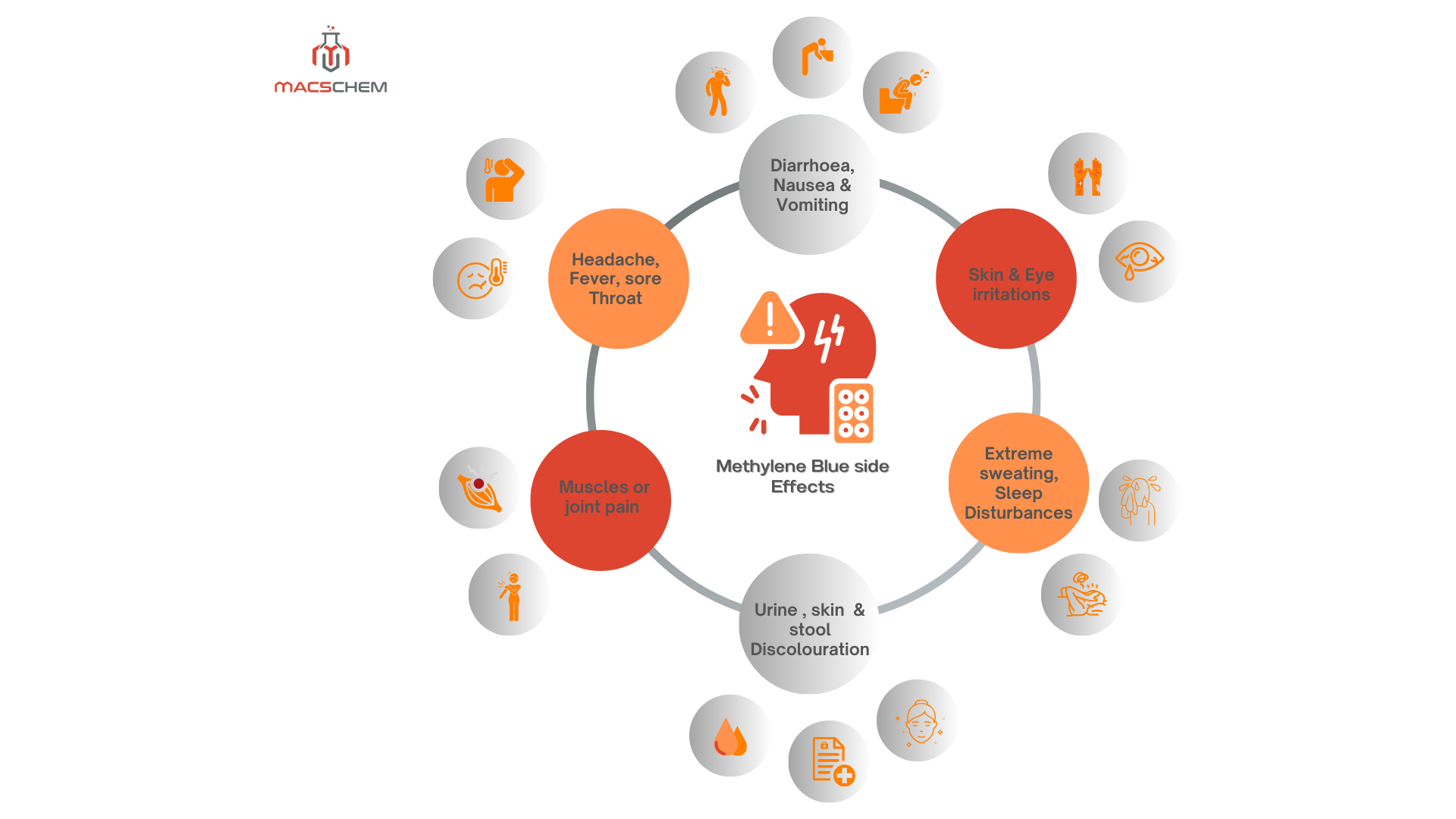
Itching & Rashes are common side effects of Methylene Blue. Redness and swelling may occur at the injection site. Skin turns bluish or greenish in color, mainly around the site of application. It also induces photosensitivity in the skin.
Prolonged use of methylene blue increases the chances of Hemolytic anemia, hepatotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Neurological effects like serotonin syndrome and cognitive impairment also have been reported.
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H303: May be harmful if swallowed H313: May be harmful in contact with skin H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness |
| Precautionary statements : | P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray P281: Use personal protective equipment as required P314: Get Medical advice/attention if you feel unwell P332+P313: If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention P308+313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention |
Methylene blue (MB), also called Methylthioninium chloride, is a tricyclic phenothiazine that belongs to the phenothiazine family. It’s a dark green powder that turns into a blue solution when dissolved in water. It is widely used as a redox indicator in chemistry because of its property of turning blue when oxidized and colorless when reduced. It is a primary treatment for methemoglobinemia, malaria, and many other pathogenic diseases. Notably, it was the first synthetic compound used as a clinical antiseptic.

CAS No.: 61-73-4; 122965-43-9
Synonyms: Methylthioninium Chloride, Basic Blue 9, Zinc free Methylene Blue, Methylene Blue Trihydrate
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C16H18N3SCl |
| IUPAC name | [7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium;chloride |
| Molecular weight | 319.85 g/mol |
| Solubility | Water, Glacial acetic acid, Glycerol, Ethanol 2%, & acetone 0.5% |
| Insoluble | Xylene & oleic acid |
| Flash point | 49°C [120°F] |
| Density | 1.230/cm3 |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Green |
| State | Crystal or powder |
| Melting point | 100-110°C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00000013(mmHg) |
| pKa | 7.5 |
| Vapour density | 1.59 at 20°C |
| pH | ~ 3 (in aqueous solution: 10 g /l, 20 °C) |
Methylene Blue slows down the aging effects of skin as it has antioxidant property. It stimulates fibroblast proliferation & promotes wound healing. It also increases the skin thickness and hydration. Studies are undergoing to check the potential of methylene blue in treatment progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome).

There are different side effects associated with the use of Methylene Blue depending upon the route of administration.

Itching & Rashes are common side effects of Methylene Blue. Redness and swelling may occur at the injection site. Skin turns bluish or greenish in color, mainly around the site of application. It also induces photosensitivity in the skin.
Prolonged use of methylene blue increases the chances of Hemolytic anemia, hepatotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Neurological effects like serotonin syndrome and cognitive impairment also have been reported.
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H303: May be harmful if swallowed H313: May be harmful in contact with skin H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness |
| Precautionary statements : | P260: Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray P281: Use personal protective equipment as required P314: Get Medical advice/attention if you feel unwell P332+P313: If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention P308+313: IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention |
Methylene blue is a medication used in treating and regulating Methemoglobinemia, and a broad range of pathogenic diseases.
Methylene Blue inhibits nitric oxide prevents beta-amyloid plaque formation, and exhibits antimicrobial properties. It enhances cognitive function and treats methemoglobinemia by improving oxygenation, with potential therapeutic benefits for Alzheimer’s and psychiatric disorders.
Methylene Blue is commonly used in chemistry as a redox indicator for analytical purposes.
The Löffler’s alkaline methylene blue staining method is a simple technique for differentiating bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. The cationic dye stains cells blue by binding to negatively charged particles like polyphosphates, DNAs, and RNAs.
The Löffler’s alkaline methylene blue staining method is a simple technique for differentiating bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. The cationic dye stains cells blue by binding to negatively charged particles like polyphosphates, DNAs, and RNAs.
Methylene Blue is excreted in the urine within 4 to 24 hours of administration, with a half-life of 5 to 6.5 hours.
Combined with nanopharmaceuticals, Methylene Blue boosts anti-cancer therapies by increasing tumor oxygen levels and enhancing sensitivity to radiation and chemotherapy.
Take each dose with a full glass of water (240 ml). Do not exceed the prescribed dose or frequency, as it won’t speed up recovery and may increase side effects.
Methylene blue is a basic thiazine dye which stains negatively charged cell components as nucleic acid.