
Bismarck brown Y is an early diazo dye first described in 1863 by Carl Alexander von Martius. It’s composed of closely related compounds, formed by the reaction of 1,3-phenylenediamine and its diazotized derivative. The synthesis process involves double diazotization of 1,3-phenylenediamine, followed by coupling to produce the dye. The compound is often a mixture of oligomers containing three or more diazo groups. Bismarck brown Y has applications in histological tissue staining, particularly for staining mucins and mast cell granules.
CAS No.:10114-58-6
Synonyms: Basic brown 1; Bismarck brown; Bismarck brown Y; C.I. 21000; C.I. Basic Brown 1, dihydrochloride; Manchester brown; Phenylene brown.
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H18N8·2HCl |
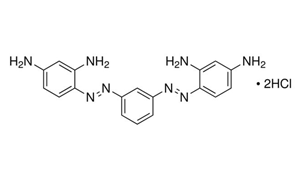
| IUPAC Name | 4-[[3-[(2,4-diaminophenyl)diazenyl]phenyl]diazenyl]benzene-1,3-diamine;hydrochloride |
| Molecular weight | 382.8g/mol |
| Solubility | Water |
| Density | 1.42±0.1 g/cm³ |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Brown |
| State | Powder |
| Melting point | >300 °C |
| λmax | 457 nm |
| pH | 2.0-4.0 |
| pKa | 4.7 |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H319: Causes serious eye irritation. |
| Precautionary statements : | P264: Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P280: Wear eye protection/ face protection. P305 + P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present, and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P337 + P313: If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/ attention. |
Bismarck brown Y is an early diazo dye first described in 1863 by Carl Alexander von Martius. It’s composed of closely related compounds, formed by the reaction of 1,3-phenylenediamine and its diazotized derivative. The synthesis process involves double diazotization of 1,3-phenylenediamine, followed by coupling to produce the dye. The compound is often a mixture of oligomers containing three or more diazo groups. Bismarck brown Y has applications in histological tissue staining, particularly for staining mucins and mast cell granules.

CAS No.:10114-58-6
Synonyms: Basic brown 1; Bismarck brown; Bismarck brown Y; C.I. 21000; C.I. Basic Brown 1, dihydrochloride; Manchester brown; Phenylene brown.
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H18N8·2HCl |
| IUPAC Name | 4-[[3-[(2,4-diaminophenyl)diazenyl]phenyl]diazenyl]benzene-1,3-diamine;hydrochloride |
| Molecular weight | 382.8g/mol |
| Solubility | Water |
| Density | 1.42±0.1 g/cm³ |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | Brown |
| State | Powder |
| Melting point | >300 °C |
| λmax | 457 nm |
| pH | 2.0-4.0 |
| pKa | 4.7 |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H319: Causes serious eye irritation. |
| Precautionary statements : | P264: Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P280: Wear eye protection/ face protection. P305 + P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present, and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P337 + P313: If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/ attention. |
Bismarck Brown Y stains acid mucins, mast cell granules, cartilage, and DNA in histological samples.
Bismarck Brown Y is used in cytology as a stain, particularly in Papanicolaou stain, to differentiate cellular components. It helps highlight specific structures like acid mucins and mast cell granules.
Bismarck Brown Y is prepared through a diazo coupling reaction. The process involves the double diazotization of 1,3-phenylenediamine, which further reacts with additional phenylenediamine molecules. This results in a mixture of azo compounds, forming the dye.
Bismarck Brown Y is employed as a counterstain in Papanicolaou stain (PAP) It helps in differentiating and highlighting the cellular components, particularly by staining the background and cytoplasmic elements to enhance the contrast of the main stain.
The Color Index (CI) number for Bismarck Brown Y is CI 21000.