

Sodium selenate is the sodium salt of selenium, known for its diverse applications in industry, nutrition, and scientific research. It is a white, water-soluble solid found in different hydrate forms, including anhydrous, heptahydrate, and decahydrate. Its decahydrate form is commonly used as a selenium supplement in multivitamins and animal feed, while its anhydrous form is used in glass manufacturing. It is synthesized through a controlled oxidation process of elemental selenium.
It is also used in biomedical research for its ability to activate protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), an enzyme that regulates protein dephosphorylation. By boosting PP2A activity it helps reduce tau protein hyperphosphorylation, a key factor in Alzheimer’s disease.
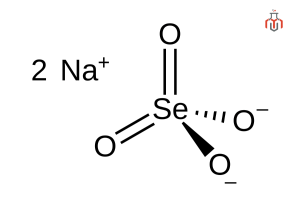
CAS No.: 13410-01-0
Synonyms: Disodium selenate; Natriumseleniat; Selenic acid, disodium salt; selenato de sodio; Sélénate de sodium; selenato di sodio
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Na2SeO4 |
| IUPAC Name | Disodium selenate |
| Molecular weight | 188.95 g/mol |
| Density | 3.098 g/cm³ |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White or grey |
| State | Solid Crystalline Powder |
| Melting point | Decomposes (NTP, 1992) |
| Selenium (Se) | 39.7 – 44.0 % |
| Sodium (Na) | 23.7 – 24.9 % |
| Purity (Titration by NaOH) | ≥ 98.0% |
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Sodium selenate (Na₂SeO₄) is being investigated for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). It reduces hyperphosphorylated tau levels in the brain.
Cancer Therapy: It has also shown potential anticancer effects in preclinical studies and early-phase clinical trials.
Pesticide: Sodium selenate is evaluated for pest control and plant disease resistance.
Bio-Fortification of Crops: It is applied as a foliar spray or via the rooting medium, often added to fertilizers, to enhance the selenium content in crops.
Dietary Supplement: It is used in livestock and poultry feed to prevent selenium deficiency and reduce the risk of white muscle disease.
Fertilizers: Na₂SeO₄ is incorporated into selenium-deficient soils to improve plant growth and human selenium intake.
Glass Manufacturing: It removes color impurities and improves optical properties in glass production.
Catalysis: It also serves as a catalyst in chemical reactions due to its oxidizing properties.
Water Treatment: Sodium selenate is studied for its ability to remove heavy metals and contaminants from wastewater.
Analytical Chemistry: It is used as a standard in laboratory analyses for selenium quantification.
| Pictograms : |    |
| Hazard Statements : | H300 + H330: Fatal if swallowed or if inhaled. |
| Precautionary statements : | P260: Do not breathe dust. P264: Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P273: Avoid release to the environment. P302 + P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water. P304 + P340 + P310: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. Immediately call a POISON CENTER/ doctor. P314: Get medical advice/ attention if you feel unwell. |
Sodium selenate is the sodium salt of selenium, known for its diverse applications in industry, nutrition, and scientific research. It is a white, water-soluble solid found in different hydrate forms, including anhydrous, heptahydrate, and decahydrate. Its decahydrate form is commonly used as a selenium supplement in multivitamins and animal feed, while its anhydrous form is used in glass manufacturing. It is synthesized through a controlled oxidation process of elemental selenium.
It is also used in biomedical research for its ability to activate protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), an enzyme that regulates protein dephosphorylation. By boosting PP2A activity it helps reduce tau protein hyperphosphorylation, a key factor in Alzheimer’s disease.

CAS No.: 13410-01-0
Synonyms: Disodium selenate; Natriumseleniat; Selenic acid, disodium salt; selenato de sodio; Sélénate de sodium; selenato di sodio
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Na2SeO4 |
| IUPAC Name | Disodium selenate |
| Molecular weight | 188.95 g/mol |
| Density | 3.098 g/cm³ |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Color | White or grey |
| State | Solid Crystalline Powder |
| Melting point | Decomposes (NTP, 1992) |
| Selenium (Se) | 39.7 – 44.0 % |
| Sodium (Na) | 23.7 – 24.9 % |
| Purity (Titration by NaOH) | ≥ 98.0% |
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Sodium selenate (Na₂SeO₄) is being investigated for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). It reduces hyperphosphorylated tau levels in the brain.
Cancer Therapy: It has also shown potential anticancer effects in preclinical studies and early-phase clinical trials.
Pesticide: Sodium selenate is evaluated for pest control and plant disease resistance.
Bio-Fortification of Crops: It is applied as a foliar spray or via the rooting medium, often added to fertilizers, to enhance the selenium content in crops.
Dietary Supplement: It is used in livestock and poultry feed to prevent selenium deficiency and reduce the risk of white muscle disease.
Fertilizers: Na₂SeO₄ is incorporated into selenium-deficient soils to improve plant growth and human selenium intake.
Glass Manufacturing: It removes color impurities and improves optical properties in glass production.
Catalysis: It also serves as a catalyst in chemical reactions due to its oxidizing properties.
Water Treatment: Sodium selenate is studied for its ability to remove heavy metals and contaminants from wastewater.
Analytical Chemistry: It is used as a standard in laboratory analyses for selenium quantification.
| Pictograms : |    |
| Hazard Statements : | H300 + H330: Fatal if swallowed or if inhaled. |
| Precautionary statements : | P260: Do not breathe dust. P264: Wash skin thoroughly after handling. P273: Avoid release to the environment. P302 + P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water. P304 + P340 + P310: IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. Immediately call a POISON CENTER/ doctor. P314: Get medical advice/ attention if you feel unwell. |
Sodium selenate is currently categorized as hazardous by the US FDA and the EU, mainly if consumed or inhaled in large doses. Chronic exposure can lead to severe lung, kidney, and liver damage
Sodium selenate is used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia, as dietary supplements and an insecticide and fungicide to control mites, aphids, and mealybugs in the glass industry.
Sodium selenate (Na₂SeO₄) and sodium selenite (Na₂SeO₃) are both selenium salts but have different oxidation states and biological activities. Sodium selenate contains selenium in the +6 oxidation state, whereas sodium selenite contains selenium in the +4 oxidation state.
Currently, sodium selenate is not an approved treatment for epilepsy. A clinical trial is underway to study sodium selenate as a treatment for drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE).
Sodium Selenate is a form of the essential trace element Selenium.
Sodium selenate is an inorganic compound.
Sodium selenate (Na₂SeO₄) and sodium selenite (Na₂SeO₃) are both selenium salts but have different oxidation states and biological activities. Sodium selenate contains selenium in the +6 oxidation state, whereas sodium selenite contains selenium in the +4 oxidation state.
No, sodium selenate is not like regular salt (sodium chloride). While both contain sodium, they have different chemical properties and functions. It’s a white, water-soluble solid that’s used in supplements and livestock feed.