

Crystal Violet is an organic chloride salt also known as Gentian Violet. It is a cationic triphenylmethane dye widely used in biological staining, treatment of microbial infection, microbiology, textile, wood & paper dyeing, and other industrial applications. Initially, it was introduced in the 19th century, and recognized for its vivid-blue violet color in water and variable shades depending on the solution’s pH. The dye’s color changes, varying from green in a slightly acidic medium to yellow in a highly acidic medium, due to the charged states of its nitrogen atoms. Moreover, it is produced via a multi-step chemical process, beginning with dimethylaniline and evolving into its distinctive cationic form. 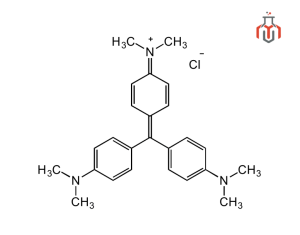
CAS No.: 548-62-9
Synonyms: Basic Violet 3; Gentian Violet; Hexamethylpararosaniline chloride; Methyl Violet 10B
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C25H30N3Cl |
| IUPAC Name | 4-{Bis[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methylidene}-N,N-dimethylcyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-iminium chloride |
| Molecular weight | 407.979 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water, Methanol & Ethanol |
| Flash point | 40 °C |
| Density | 1.19 g/cm³ at 20°C |
| pH | 2.5-3.5 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Green |
| State | Crystal or powder |
| Melting point | 205 °C |
| λmax | 590nm |
| LogP | 1.172 at 25℃ |
| pka | 9.4(at 25℃) |
| Pictograms : | |
| Hazard Statements : | H302: Harmful if swallowed. |
| Precautionary statements : | P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. |
Crystal Violet is an organic chloride salt also known as Gentian Violet. It is a cationic triphenylmethane dye widely used in biological staining, treatment of microbial infection, microbiology, textile, wood & paper dyeing, and other industrial applications. Initially, it was introduced in the 19th century, and recognized for its vivid-blue violet color in water and variable shades depending on the solution’s pH. The dye’s color changes, varying from green in a slightly acidic medium to yellow in a highly acidic medium, due to the charged states of its nitrogen atoms. Moreover, it is produced via a multi-step chemical process, beginning with dimethylaniline and evolving into its distinctive cationic form. 
CAS No.: 548-62-9
Synonyms: Basic Violet 3; Gentian Violet; Hexamethylpararosaniline chloride; Methyl Violet 10B
Resources: Biological Stains | Classification, Examples & Uses
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C25H30N3Cl |
| IUPAC Name | 4-{Bis[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methylidene}-N,N-dimethylcyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-iminium chloride |
| Molecular weight | 407.979 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water, Methanol & Ethanol |
| Flash point | 40 °C |
| Density | 1.19 g/cm³ at 20°C |
| pH | 2.5-3.5 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Green |
| State | Crystal or powder |
| Melting point | 205 °C |
| λmax | 590nm |
| LogP | 1.172 at 25℃ |
| pka | 9.4(at 25℃) |
| Pictograms : | |
| Hazard Statements : | H302: Harmful if swallowed. |
| Precautionary statements : | P202: Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. |
In Gram staining, crystal violet stains all bacteria purple, but Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet dye due to their thick peptidoglycan layer.
Crystal Violet is a basic dye, and has a positive charge which allows it to bind to the negatively charged components of the cell for instance nucleic acids and cell walls, making it much more effective in microscopy.
Leaving crystal violet on too long can cause over-staining, making it difficult to differentiate cell types and leading to inaccurate Gram staining results.
It has been used in topical antifungal treatments, but regulations vary.
The principle of the crystal violet assay is to quantify biofilm formation by staining the cells attached to a surface with crystal violet dye.
Crystal violet changes colour at different pH levels. At a pH of +1.0, it appears green, while in strongly acidic solutions (pH −1.0), it turns yellow. Further, around pH 11 to 12 bluish-purple colour is observed.
To remove the stain of crystal violet ( gentian violet ) from lips, use oil-based removers like coconut oil, baby oil, baking soda, or a cotton ball dipped in hydrogen peroxide.