Importing chemicals to the USA is profitable but intimidating, especially for those new to international trading. The process is infused with regulations, rigorous safety protocols, often changing trade policies, and a need to acquire all the licenses and certifications. It is crucial to comprehend these essential elements and understand all the vital factors.
Regulatory Compliance
When bringing chemicals into the United States, the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) requires importers to abide by the rules set by the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). To clear customs smoothly, ensure you have all the necessary paperwork, including TSCA certifications. If you want to avoid delays and ensure everything goes according to plan, the regulations of the following federal agencies are essential. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and TSCA are all government agencies that keep an eye on chemical imports.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
FDA is a federal agency of the US, which oversees public health protection by ensuring the efficacy, safety, and security of human and veterinary drugs, medical devices, biological products, food, cosmetics, and radioactive products.
The Environmental Protection Act (EPA)
EPA, a US federal agency started in 1970, is assigned to environmental and human health protection. It sets regulations to restrain pollution, manages hazardous wastes, and oversees land, water, and air quality. Further, they also conduct research, spread awareness among the public regarding environmental issues, and monitors compliance with laws, imposing penalties for violations.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
The OSHA is a US-based federal agency, which is responsible for safe and healthful working conditions for the people by setting and compelling standards providing training and education, and executing workplace safety programs for employers.
The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)
The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) became law on October 11, 1976, and became official on January 1, 1977. It oversees the manufacture, importation, distribution, processing, use, and disposal of chemical substances in the United States. TSCA authorizes the EPA to regulate the testing of chemicals for potential toxic effects before they are commercially manufactured or distributed.
When importing chemicals to the US, you must certify it according to the TSCA inventory stating whether:
- Complies with TSCA: Approved as positive certification
- Non-complies with TSCA: Approved as negative certification
Failure to give the correct certification causes a delay or even the decline of entry.
Adherence to specific chemical regulations-
There are specified TSCA regulations, significant to certain chemicals which include:
- Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): In 1979 TSCA banned the manufacturing, processing, distribution, or use of PCBs. However, it permits the inadvertent production of PCBs. (https://www.epa.gov/pcbs/learn-about-polychlorinated-biphenyls)
- Asbestos: TSCA regulates the manufacture, importation, processing, and distribution of asbestos as it causes harmful health effects, especially lung cancer. (https://www.epa.gov/asbestos/learn-about-asbestos#asbestos)
- Lead: TSCA has regulations regarding lead in paint, plumbing materials, and other products as it causes various health effects to humans and animals. (https://www.epa.gov/lead/learn-about-lead)
- Mercury: Mercury is considered to be a neurotoxin. So Title I of TSCA inhibits the sale, distribution, or transfer of radical mercury by federal agencies. (https://www.epa.gov/mercury)
- Formaldehyde: TSCA regulates the manufacture, processing, distribution, and use of formaldehyde as it irritates the skin, eyes, nose, and throat, also constant exposure to it may cause some cancer. (https://www.epa.gov/formaldehyde/facts-about-formaldehyde#whatare)
- Radon: According to EPA analysis radon is the primary cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, it is responsible for 21,000 lung cancer deaths every year. Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that is found in buildings and poses health risks (https://www.epa.gov/radon)
Certification Requirements
Depending on certain chemicals and their specific uses, various certificates are required. Here are some general examples:
FDA certification
- FDA Food Facility Registration: For food products.
- FDA Medical Device Listing: For medical devices.
- FDA Cosmetic Registration: For cosmetics.
- FDA Drug Listing: For drugs
EPA certifications
- EPA Pesticide Registration: For pesticides.
- EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory: For chemicals listed on the TSCA Inventory.
- EPA Registration for Pesticide Active Ingredients: For manufacturers of pesticide active ingredients.
OSHA certifications
- OSHA Hazard Communication Standard: For businesses that handle hazardous chemicals.
- OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard: This is for businesses that handle potentially infectious materials.
- International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations: These are required if you are transporting substances via airways.
- International Maritime Organization (IMO) Code of Practice for the Safe Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Sea: These are essential if you are transporting through sea or waterways.
- DOT Hazardous Materials Regulations: If you want to transport your goods by road or rail the US Department of Transportation is efficient, safe, sustainable, and upright.
- ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System: Implementing ISO 9001 signifies that your firm has established effective methods and qualified workers to deliver perfect products and services from time to time.
- ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System
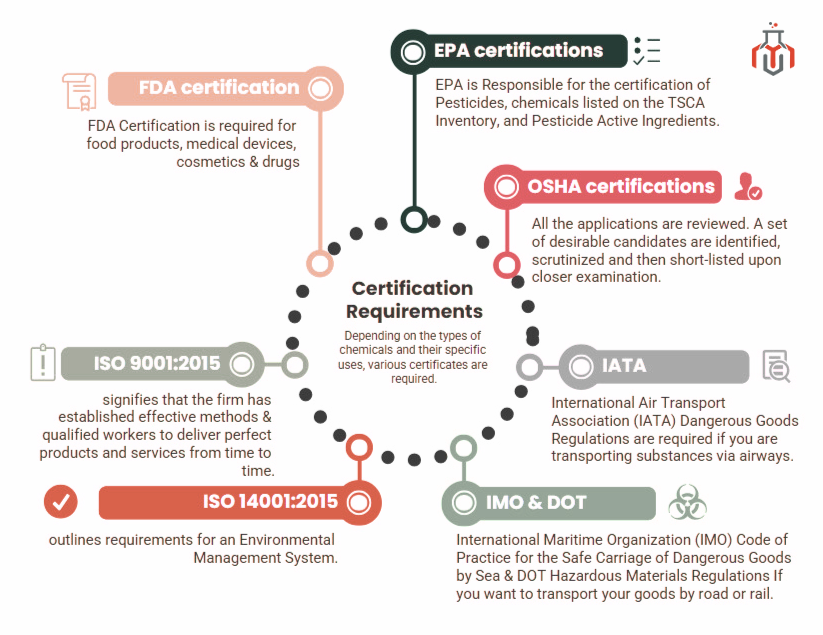
The certifications mentioned above may vary depending on the chemicals imported and their intended use. Thus, it’s crucial to do in-depth research before importing.
Documentation
- TSCA import certification: As mentioned earlier, positive and negative certification accompany shipments of TSCA-regulated chemicals.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Mention detailed information about the chemicals, including their hazards, safe handling, and emergency procedures.
- Notice of Arrival (NOA): An NOA must be filed for some chemicals with the EPA, particularly pesticides.
- Bill of Lading (BoL): The receipt from the shipment company listing the volume of your products, shipment’s contents, and destination.
- Commercial Invoice: A record outlining the agreement between seller and buyer, consisting of product details, cost, and terms of sale.
- Packaging list: Describe precisely what’s in the package including weight and size. During the survey, CBP can compare this to the original shipment in search of errors and criminal activities.
- Entry Forms (CBP Form 7533 or CBP Form 3461): When entering goods into the US, CBP asks for these, as this gives information about the imported goods and the carrier transporting them.
Additional documents that may be required
- Arrival Notice
- Import License
- Purchase Order & the Credit Letter
- Test report
- Industrial License
- Health Status Documents (if importing animals or plant-based foods across international borders)
- GATT/DGFT Declaration
Importing Hazardous Chemicals
For importing hazardous chemicals extra precautions and abiding by specific regulations are essential:
- Safe Transportation: Abide by the transport rules set by the Department of Transportation for dangerous materials.
- Proper Labeling: Make sure that the chemicals are correctly labeled with GHS hazardous symbols and statements.
- Emergency Response Planning: Create an extensive emergency response to address latent incidents.
- Storage & Handling: Store hazardous chemicals in suitable conditions and give proper instructions.
- Obtain Required permits: You may need additional licenses or permits depending on the hazardous chemicals. For instance, certain chemicals may need to obtain permits from EPA, OSHA, or other regulatory agencies.
Pre-Shipment Verification
Before importing chemicals to the US, you should rigorously regulate inspections to determine potential issues and assure compliance. This comprises-
- Pre-shipment inspection (PSI): PSI certifies the quality, quantity, packaging, and labeling of goods before shipping. PSI helps ensure that the goods meet the regulatory requirements and agreed-upon statements.
- MSDS/SDS certificate: MSDS certification is requisite for exporting chemicals or products containing hazardous substances.
- Pre-manufacture notices (PMN) or significant new use rules (SNURs): Determine if the chemicals are prone to PMN & SNURs.
Customs Brokerage
A Customs broker is an essential part of international trade as they offer unique services, and play a vital part in international trade and transport ensuring that exported & imported chemicals adhere to rigorous regulations and enable smooth approval. Their expertise and assistance offer several advantages.
- Expertise: Custom broker retains extensive knowledge of customs regulations, processes, and specified requirements for chemical imports.
- Time-saving: They save good time, by managing the complex custom clearances procedures.
- Cost-effectiveness: Customs brokers analyze potential cost-saving methods through efficient procedures and negotiation.
- Risk mitigation: They help inhibit the risk related to non-compliance, such as fines, penalties, or delays.
How to choose a customs broker?
When appointing a customs broker, keep these points in mind –
1. Select a licensed customs broker.
2. It’s essential to hire a broker with experience in the product or chemical which you are importing/exporting, they will guide you much better than the generic customs broker.
3. Your customs broker should have know-how about the local, regional, and even global government authorities to manage the customs process that differ from country to country.
Key Services provided by customs broker include:
- Documentation Assistance
- Regulatory assistance
- Custom Clearance
- Trade compliance
Employing a customs broker can streamline your chemical import/export procedures by ensuring compliance and decreasing risk.
Importer of Records (IOR)
An importer of records is your legal confront for the import shipment when dealing with US customs. They make sure that all import regulations are followed, for a smooth custom-clearance.
Importer of Record’s Responsibility
- Compliance: IOR operates the to-do list by analyzing duties, securing payments, and ensuring proper documentation.
- Regulation: They navigate various regulations set by the agencies like FDA, EPA, & DOT, assuring your goods meet all safety and environmental grade.
- Recordkeeping: The IOR carefully sustains your import transaction records for at least five years.
Key points to remember:
- The IOR isn’t always the buyer of the goods.
- While the consignee receives the shipment, the IOR is liable for customs clearance.
- Authorization of the goods depends upon the condition, it can be temporary for the IOR or permanent for the final recipient.
Selecting the right IOR :
- Look for expertise in managing import regulations and recordkeeping.
- For better counseling look for an IOR with experience in your industry.
- Inquire regarding logistic support, power of attorney services, and complete service coverage.
By carefully comprehending the role of IOR, you can ensure regulated import procedures for your goods.
Importing Non-TSCA Regulated Products (FDA)
If you are importing chemicals that don’t abide by the TSCA regulations such as medical devices, cosmetics, and food, your products will probably fall under the domain of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Key FDA considerations
- Product Classification: Specifically distinguish your product to specify which FDA regulations are implemented to them.
- Regulatory compliance: Make sure your products meet all suitable FDA norms including safety, labeling, and manufacturing requirements.
- Premarket Notification: For specific medical devices, you may need to apply for a premarket notification (510(k)) to the FDA.
- Import documentation: Arrange all required documents such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of analysis.
- FDA import regulations: Follow the FDA import regulations, which may comprise inspection and detention.
Employing a customs broker can aid you in determining the complex FDA regulations, securing smooth customs clearance, preparing and submitting documents, and guiding with customs clearance which can smoothly import non-TSCA regulated goods into the US.
Additional points to Consider
- Environmental Impact Assessments: For certain products that might impact our environment, you may need to regulate environmental impact assessments and abide by relevant environmental regulations.
- Staying updated on new Regulations: The chemical import guidelines keep changing frequently. Stay acquainted regarding trends and challenges, such as:
Digitalization: Leverage technology to organize procedures and enhance effectiveness.
Sustainability: Manage increasing concerns about environmental impact.
Regulatory Changes: Keep up with the evolution in regulations and industry standards.
- Sustaining regulations and averting penalties: Constantly analyze your import processes to ensure compliance with all regulations. Consider using the compliance management systems to follow changes and stay up-to-date.
For more detailed information, please consult the FDA Website: https://www.fda.gov/
FAQs
Q. Where do I need to register my chemicals before importing them into the US?
Before importing chemicals into the U.S., proper registration must be done with governing bodies like EPA, TSCA, and U.S. Customs and Border Protection. Each Agency has its own application forms and procedures which need to be followed depending upon the item being imported.
Q. Is there any special guideline for hazardous chemicals?
For hazardous chemicals, there are specific guidelines from the OSHA and TSCA. There are also Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) that govern the transportation of hazardous materials.
Q. Which chemicals are subject to TSCA import?
Chemicals like Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), Asbestos, Radon, Lead, Mercury, and Formaldehyde are under the specified TSCA regulations.
Q. What safety guidelines should be followed when importing chemicals into the U.S.?
To import chemicals into the U.S., companies carefully fill out the registration and get the certifications from TSCA and EPA. The form must be included with the airway bill and shipper declaration for the chemical. The instructions concerning invoicing, packaging, marking, and labeling should be properly followed.
Q. Are purchasers of items from importers (or customers of importers) required to make any certification?
The purchasers/customers of importers are not required to submit any certifications. Importers are liable to complete all the formalities and procedures.
Q. Who must get the TSCA certification for U.S. Customs?
The importer of record or a Customs house broker with power of attorney acting as the importer’s agent is responsible for TSCA certification.
Q. Do chemical substances imported solely for R&D use also require TSCA certification?
All the substances which are for a use governed by TSCA, require a positive TSCA certification.
Resources