

Phenol red, also known as phenolsulfonphthalein (PSP), is a pH indicator often used in cell biology and laboratories. It is a stable red crystal, which acts as a weak acid with a pKa of 8.00 at 20°C. In solution, phenol red switches from yellow to red as the pH shifts from 6.8 to 8.2, turning bright pink at higher pH levels. Its structure exhibits a zwitterion form under very acidic conditions. Further, it has similarities with other pH indicators like bromothymol blue and phenolphthalein.
CAS No.: 143-74-8
Synonyms: Phenolsulfonphthalein; Fenolipuna; Sulfonphthal; Sulphental; Sulphonthal; Phenolsulphonphthalein; Phenolred
| Physical Properties | |
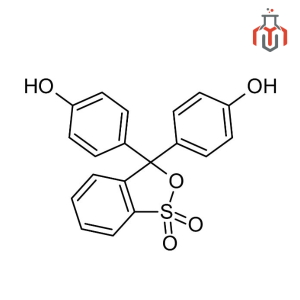
| Chemical formula | C19H14O5S |
| IUPAC Name | 4-[3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,1-dioxo-2,1λ6-benzoxathiol-3-yl]phenol |
| Molecular weight | 354.38 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water, Alcohol, Aq. alkali hydroxides and Carbonates |
| Flash point | 294.2±30.1 °C |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm³ |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Red to Dark Brown |
| State | Solid powder |
| Melting point | >300°C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| pH | Below 6.8(Yellow) 6.8–8.2(Red) Above 8.2(Bright pink or fuchsia) |
| LogP | 3.02 |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H315: Causes skin irritation. H335: May cause respiratory irritation. |
| Precautionary statements : | P261: Avoid breathing dust. P352: Wash with plenty of water. |
Phenol red, also known as phenolsulfonphthalein (PSP), is a pH indicator often used in cell biology and laboratories. It is a stable red crystal, which acts as a weak acid with a pKa of 8.00 at 20°C. In solution, phenol red switches from yellow to red as the pH shifts from 6.8 to 8.2, turning bright pink at higher pH levels. Its structure exhibits a zwitterion form under very acidic conditions. Further, it has similarities with other pH indicators like bromothymol blue and phenolphthalein.

CAS No.: 143-74-8
Synonyms: Phenolsulfonphthalein; Fenolipuna; Sulfonphthal; Sulphental; Sulphonthal; Phenolsulphonphthalein; Phenolred
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H14O5S |
| IUPAC Name | 4-[3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,1-dioxo-2,1λ6-benzoxathiol-3-yl]phenol |
| Molecular weight | 354.38 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water, Alcohol, Aq. alkali hydroxides and Carbonates |
| Flash point | 294.2±30.1 °C |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm³ |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Colour | Dark Red to Dark Brown |
| State | Solid powder |
| Melting point | >300°C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| pH | Below 6.8(Yellow) 6.8–8.2(Red) Above 8.2(Bright pink or fuchsia) |
| LogP | 3.02 |
| Pictograms : |  |
| Hazard Statements : | H315: Causes skin irritation. H335: May cause respiratory irritation. |
| Precautionary statements : | P261: Avoid breathing dust. P352: Wash with plenty of water. |
Phenol Red is a pH indicator that is used in laboratory applications. It appears red in neutral to alkaline solutions and turns yellow in acidic conditions.
Positive phenol red indicates a pH change in a solution, typically signifying an alkaline condition. In tests, it is used to show that the environment is more basic, with phenol red turning red or pink.
Phenol red changes color because it loses protons as pH increases. It changes from yellow at pH below 6.6 to red between pH 6.6 and 8.0 and turns bright pink (fuchsia) above pH 8.1.
A phenol red test indicates the pH level of a solution. It changes color in response to pH changes, helping to distinguish if a solution is acidic, neutral, or basic.
Phenol red tablets are used to test the presence of a certain medium or to monitor pH levels in various solutions. They help in assessing the acidity or alkalinity of a sample.
A Phenol Red broth should typically be incubated and observed within 24 to 48 hours for accurate results.